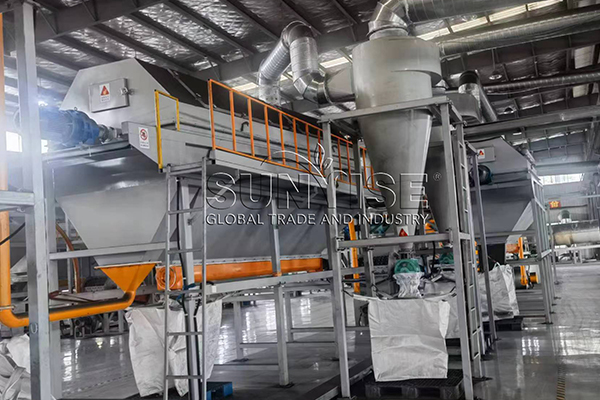
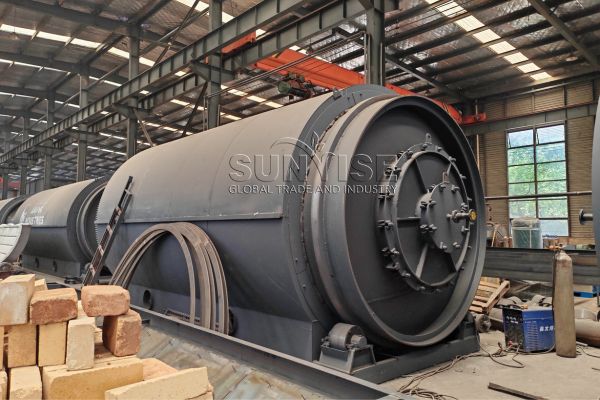
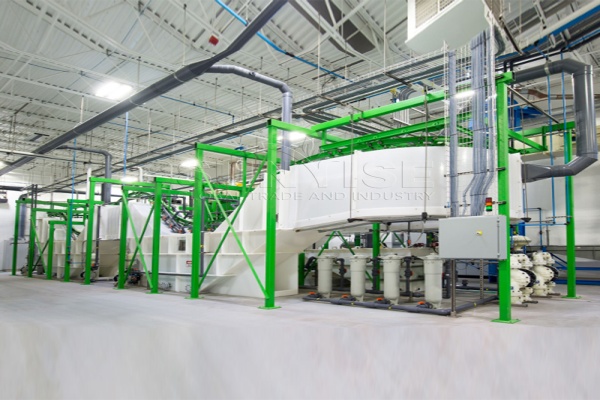
Industrialization has led to the invention of many electrical and electronic devices that have made our lives relatively easy. This has led to an increase in the generation of electronic waste (déchet électronique). Dans 2019, the global generation of e-waste was about 53.6 million tons, and it is expected to reach 74 million tons by 2030. Dans 2019, Asia, America, and Europe generated 50 million tons of e-waste, while Africa and Oceania generated 2.9 million tons and 0.7 million tons, respectivement. Donc, what is considered e-waste? Si vous avez un intérêt, Veuillez continuer à lire.
D'abord, check this video. Then you can get a preliminary understanding of the current situation of e-waste……
Definition of e-waste

Electronic waste, commonly known as e-waste, has received increasing attention in recent years for its far-reaching social, environmental and economic impacts. With the rapid development of electronic devices and consumers constantly upgrading their electronic products, the amount of e-waste generated has surged.
E-waste announced by the European Commission includes discarded electronic and electrical equipment. This type of waste includes a variety of technological products that have exceeded their service life or are inefficient. Electronic devices contain harmful elements and, unlike ordinary garbage generated in cities, they pose a major threat to ecosystems and human health.
Many countries, especially developing countries, lack the infrastructure to properly handle and recycle e-waste, leading to environmental and health risks caused by improper e-waste disposal. Actuellement, many people use dangerous methods such as open burning, landfilling, open dumping, informal dismantling and manual recycling. These practices pose a significant risk to public health. In order to avoid the high cost of proper disposal, many developed countries choose to export e-waste to developing countries such as India and Africa. These countries are currently struggling with the problem of insufficient infrastructure for e-waste management.
What are the recyclable e-wastes?
Lithium batteries
Because lithium batteries contain a lot of reusable materials:
Lithium: Lithium is a key component of lithium batteries, and recycled lithium can be used to make new lithium batteries. Par exemple, in electric vehicles and portable electronic devices, the recycling and reuse of lithium is essential to reduce raw material costs and ensure the supply of lithium resources.
Cobalt: De nombreuses batteries au lithium contiennent du cobalt dans les matériaux d'électrode positive, comme l'oxyde de cobalt au lithium (LICOO₂). Le cobalt est un métal rare et cher, et le cobalt recyclé peut être réutilisé dans l'industrie de la fabrication de batteries, Réduire la dépendance aux ressources de cobalt nouvellement extraites.
Nickel: Quelques batteries au lithium (comme l'oxyde de nickel-cobalt-manganisé (NCM) batteurs) contenir le nickel. Le recyclage du nickel aide à recycler les ressources, Et dans la production de nouvelles batteries, Le nickel recyclé peut répondre à certains des besoins en matière première.
Cuivre et aluminium: Le cuivre et l'aluminium sont généralement utilisés dans les parties de connexion du boîtier et des électrodes des batteries au lithium. Ces métaux peuvent être purifiés par des processus de recyclage, puis réutilisés dans la fabrication électronique des équipements ou d'autres utilisations industrielles.
Méthodes de recyclage:
Ligne de production de recyclage des batteries au lithium Includes steps such as disassembly, crushing and screening. D'abord, disassemble the waste lithium battery, separate the shell, electrode and other parts, then crush the electrode material, and separate copper, aluminum and other metals by screening and magnetic separation.
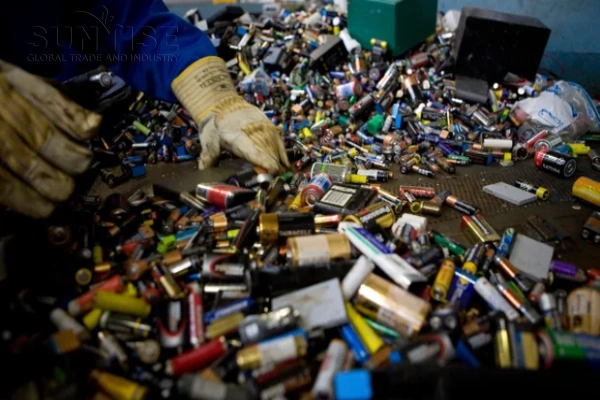
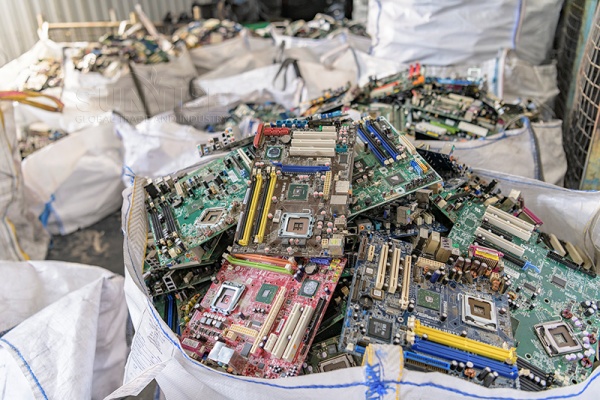
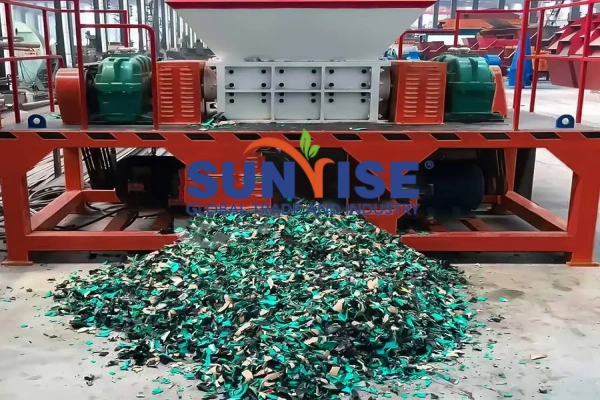




Circuit board
Recycled materials:
Precious metals: Circuit boards contain precious metals such as gold, argent, and platinum. Gold is mainly used for pins, contacts and connection parts of some high-precision electronic components on circuit boards because it has good conductivity and corrosion resistance. Silver is often used in circuit boards and some components such as capacitors. These precious metals have high recycling value and can be reused in industries such as electronic component manufacturing or jewelry.
Métaux non ferreux: Le cuivre est le métal non ferreux le plus important dans les cartes de circuits imprimés et est utilisé pour fabriquer des circuits et des fils de connexion de divers composants électroniques. Le cuivre recyclé peut être utilisé pour fabriquer de nouveaux fils, câbles et composants électroniques. En outre, les cartes de circuits imprimées contiennent également une petite quantité de boîte, qui est principalement utilisé pour le soudage des composants électroniques. L'étain recyclé peut être utilisé à nouveau dans la production de matériaux de soudage.
Métaux rares: Comme le tantale, qui est utilisé dans certains condensateurs hautes performances sur les cartes de circuits imprimées. Le recyclage de Tantalum contribue à répondre à une partie de la demande de métaux rares dans l'industrie de l'électronique car les ressources de tantale sont relativement rares.
Méthode de recyclage des panneaux de circuit:
D'abord, démonter la carte de circuit imprimé pour éliminer les grands composants, and then break the circuit board into small particles. Then use physical sorting methods such as gravity sorting, magnetic separation and electrostatic sorting to separate different metals and non-metallic materials.
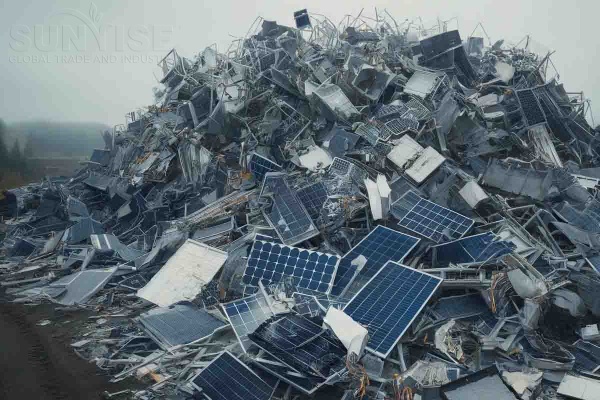
Solar panels
Recyclable materials:
Silicon: Silicon is the main material of photovoltaic panels, especially in crystalline silicon photovoltaic panels. Recycled silicon can be reused in photovoltaic panel manufacturing after purification and other processes, or used in other semiconductor-related industries.
Silver: The electrode part of photovoltaic panels usually contains silver, which is used to collect and conduct current. Recycled silver can be used to make new photovoltaic panel electrodes or conductive parts of other electronic devices.
Aluminum: The frame of photovoltaic panels is usually made of aluminum, et l'aluminium recyclé peut être utilisé pour fabriquer de nouveaux cadres de panneaux photovoltaïques ou d'autres produits en aluminium.
Verre: Le panneau de panneaux photovoltaïques est principalement en verre. Le verre recyclé peut être utilisé dans des industries telles que le verre architectural et le verre automobile après le nettoyage et le traitement.
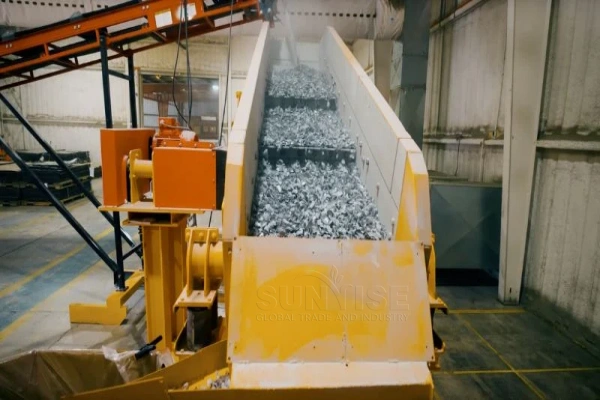
Comment Recycler le panneau solaire des déchets:
D'abord, Utilisez un dissolvant de cadre pour démonter le panneau photovoltaïque et des composants séparés tels que le verre, Crame d'aluminium et cellules de batterie. Une fois le verre retiré, Le panneau photovoltaïque est écrasé avec un broyeur. Les plaquettes de silicium séparées des cellules de la batterie sont d'abord écrasées et broyées en particules ou poudres plus petites, puis dépisté à l'aide d'équipement de dépistage pour filtrer le silicium, cuivre, et la colle Eva.


Politiques de recyclage des déchets électroniques
Let’s take some countries as examples!
| Country | Policy | Outcome | |
| 1. | United States | State level E-waste Laws | Approach towards minimized inconsistent recycling and illegal dumping |
| 2. | Germany | Extended Producer responsibility (EPR) | High rates of recycling, with reduced illegal dumping |
| 3. | Sweden | Producer responsibility with fees | Effective collection and recycling system |
| 4. | Chine | National E-waste Recycling program | Efforts to formalize the recycling sector, and reduction of environmental pollution |
| 5. | Inde | E-waste Management rules 2016 | Towards implementation and development of compliance |
Summary
The mountains of discarded electronics are not only an eyesore, but also a potential concern for our health and our planet. En même temps, electronic waste recycling has great potential because it is able to extract valuable metals, which are present in higher concentrations in electronic waste than in their natural sources. En outre, the technology of different electronic waste recycling methods optimizes the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of these methods. These methods involve electronic products such as circuit boards, panneaux photovoltaïques, batteries au lithium, etc..
There is still a lot of work need to do to develop sustainable and efficient electronic waste management solutions. As a professional e-waste recycling machine manufacturer, SUNRISE is also working hard to cope with the growing problem of e-waste management. SUNRISE’s e-waste recycling production lines are helping lots of clients to save resources and generate economic benefits. En même temps, we will adjust the proposal according to the situation of the customer’s country to ensure that every customer can get the most efficient electronic waste recycling production line.
Donc, please do not hesitate to Contactez-nous, we’ll give you advice from a professional perspective.
Contactez-nous